
The ratio is calculated on a “cash basis” as it considers the actual cash that a business has to meet its debt obligations. It is similar to the normal TIE, except that TIE-CB uses adjusted operating cash flow instead of EBIT. We could also use Times Interest Earned (Cash Basis) (TIE-CB) to get an even clearer picture. Finally, in case of simple interest method, the interest expense during a period can be calculated using the formula as, Interest expense SI P t r. Depreciation and amortization are non-cash expenses, and thus, they don’t impact the cash position. Non-cash expenses Depreciation and amortisation. It shows a specific aspect of a companys cost. Interest expense Interest paid on borrowings like loans, line of credit, bonds, etc. In place of EBIT, one may use EBITDA (earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization) to get the real cash position. Interest Expense (interest expense percentage) shows interest expenses as a percentage of gross income. expense would be added back to tentative taxable income in determining ATI. It primarily focuses on the company’s short-term ability to meet the interest payment as it is based on the current earnings and expenses. Specifically, any expense or loss is economically equivalent to interest to.The Motley Fool If a company has 100 million in debt with an average. TIE may show a favorable number even if the business is facing a principal payment that is big enough to eat up all EBIT. The simplest way to calculate interest expense is to multiply a company's total debt by the average interest rate on its debts. The metric does not take into account any upcoming principal payment.To avoid this, one should calculate the interest using the rate given on the face of the bonds. It is the price that a lender charges a borrower for the use of the lenders money. For instance, it may include a discount or premium on the sale of bonds. Interest expense relates to the cost of borrowing money. The interest expense figure is also an accounting calculation and may not reflect the actual interest expenses.We set up the following Excel formula to handle this case. On the other hand, it may also happen that the ratio may come low even if the business has significant positive cash flows. The Interest Expense and Interest Income appear on the companys Income Statement, and the. It is possible that much of the sales of the business are on a credit basis. This paragraph (c)(4) provides rules for determining when debt proceeds are. EBIT does not actually mean the cash generated by the business. (B) Interest expense allocated to a passive activity expenditure (as defined. Using EBIT to calculate TIE does not give a clear picture.A negative ratio means the company is not financially sound.The increase of interest payable 7,000 is considered as cash inflow. The Net Income balance already deducts 20,000 of interest expense. Interest payable increase from 10,000 to 17,000 at the end of the year. It can help to compare the two companies. Note: We already know that the interest paid is 13,000 but why we only see 7,000 appear on the cash flow statement.Explanation of the Interest Expense Formula.
The ratio indicates the solvency of a company. Total amount paid for Interest INR (4,669.88 + 104.29) Cr INR 4,774.17 cr.

The controller issues financial statements each quarter, and wants to know the amount of the interest expense for the past three months.
#Interest expense formula how to#
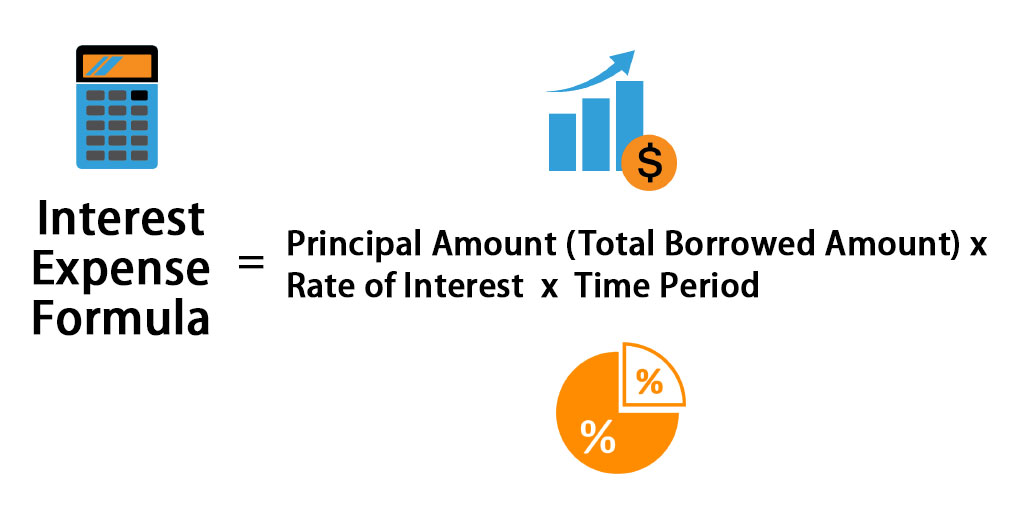
Principal x Interest rate x Time period = Interest expense Example of How to Calculate Interest Expenseįor example, a company has borrowed $85,000 at a 6.5% interest rate. The formula for total interest is Total Interest Interest Paid + Interest on Unpaid Interest Total Loan Amount Principle. Use the interest formula to arrive at the interest expense. To calculate interest expense, follow these steps:ĭetermine the amount of principal outstanding on the loan during the measurement period.ĭetermine the annualized interest rate, which is listed in the loan documents.ĭetermine the time period over which the interest expense is being calculated. It may be associated with a variety of financing instruments, including loans, convertible debt, lines of credit, and bonds. If a company has 100 million in debt with an average interest rate. This can be done by calculating the interest rate per month and dividing that by 2, to arrive at the half monthly interest expense. The simplest way to calculate interest expense is to multiply a company's total debt by the average interest rate on its debts. Interest expense is the cost of the funds that have been loaned to a borrower. To account for the interest expense that has been incurred from 16th June to the 30th June 2020, the company needs to calculate the interest expense for the period.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
